Advancements in Indigenous Metal 3D Printing Technology for Defence and Aerospace Applications
Indigenous Metal 3D Printer for Defence, Aerospace Applications Developed by IIT Jodhpur
In recent years, there has been a growing demand for advanced manufacturing technologies in the defence and aerospace sectors. One such technology that has gained significant attention is metal 3D printing. This innovative technique allows for the creation of complex metal parts with high precision and efficiency. Recognizing the potential of this technology, the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Jodhpur has developed an indigenous metal 3D printer specifically designed for defence and aerospace applications.
The development of this metal 3D printer marks a significant milestone in the advancement of indigenous manufacturing capabilities in India. With this technology, the country can reduce its dependence on imported components and strengthen its self-reliance in the defence and aerospace sectors. The printer is capable of producing high-quality metal parts that meet the stringent requirements of these industries.
One of the key features of this indigenous metal 3D printer is its ability to work with a wide range of metal alloys. This versatility allows for the production of parts with varying mechanical properties, making it suitable for a wide range of applications. Whether it is a lightweight component for an aircraft or a high-strength part for a missile, this printer can handle it all.
Moreover, the printer is equipped with advanced sensors and monitoring systems that ensure the quality and consistency of the printed parts. This is crucial in industries where even the slightest defect can have catastrophic consequences. With this technology, manufacturers can have confidence in the reliability and performance of the printed parts.
Another advantage of this indigenous metal 3D printer is its cost-effectiveness. Traditional manufacturing methods often involve complex machining processes that are time-consuming and expensive. In contrast, metal 3D printing eliminates the need for many of these processes, resulting in significant cost savings. This is particularly beneficial for defence and aerospace industries that require large quantities of high-quality metal parts.
Furthermore, the printer is designed to be user-friendly, allowing even non-experts to operate it with ease. This is a crucial factor in industries where skilled labor is often in short supply. With this technology, manufacturers can streamline their production processes and reduce the time and effort required to produce complex metal parts.
The development of this indigenous metal 3D printer is a testament to the capabilities and expertise of the researchers at IIT Jodhpur. Their dedication and hard work have resulted in a technology that has the potential to revolutionize the defence and aerospace industries in India. With this printer, the country can not only meet its domestic requirements but also become a global player in the field of metal 3D printing.
In conclusion, the development of an indigenous metal 3D printer by IIT Jodhpur is a significant advancement in the field of manufacturing technology. This printer has the potential to transform the defence and aerospace industries in India by providing high-quality, cost-effective, and versatile metal parts. With this technology, the country can reduce its dependence on imports and strengthen its self-reliance. The researchers at IIT Jodhpur have truly made a remarkable contribution to the advancement of indigenous manufacturing capabilities in India.
IIT Jodhpur’s Groundbreaking Contribution to Metal 3D Printing in Defence and Aerospace Sectors
IIT Jodhpur, one of India’s premier technical institutions, has made a groundbreaking contribution to the field of metal 3D printing. The institute has developed an indigenous metal 3D printer that is specifically designed for defence and aerospace applications. This development is a significant milestone in the country’s efforts to enhance its capabilities in these critical sectors.
Metal 3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a revolutionary technology that allows for the creation of complex metal parts with high precision. It has the potential to transform the manufacturing industry by reducing costs, improving efficiency, and enabling the production of customized components. However, the technology has been primarily dominated by foreign manufacturers, making it difficult for Indian industries to fully leverage its benefits.
Recognizing this gap, IIT Jodhpur took up the challenge of developing an indigenous metal 3D printer that meets the specific requirements of the defence and aerospace sectors. The institute’s team of researchers and engineers worked tirelessly to design and build a printer that is not only capable of printing metal parts but also meets the stringent quality and performance standards demanded by these sectors.
The result of their efforts is a state-of-the-art metal 3D printer that is capable of printing complex metal parts with high precision and accuracy. The printer utilizes a combination of advanced technologies, including laser sintering and powder bed fusion, to create parts layer by layer. This allows for the production of intricate geometries and complex structures that are difficult to achieve using traditional manufacturing methods.
One of the key advantages of the indigenous metal 3D printer developed by IIT Jodhpur is its ability to work with a wide range of metal alloys. This flexibility is crucial in the defence and aerospace sectors, where different alloys are often used for specific applications. The printer can handle materials such as titanium, aluminum, stainless steel, and nickel-based superalloys, among others, ensuring that it can meet the diverse needs of these sectors.
In addition to its versatility, the printer also offers several other benefits. It has a large build volume, allowing for the production of large-sized components. It also has a high printing speed, enabling faster turnaround times. Moreover, the printer is equipped with advanced monitoring and control systems, ensuring that the printing process is closely monitored and any deviations are immediately addressed.
The development of this indigenous metal 3D printer is a significant achievement for IIT Jodhpur and a testament to the institute’s commitment to innovation and research. It not only showcases the technical expertise of the institute’s researchers and engineers but also highlights the potential of Indian institutions to contribute to the country’s defence and aerospace sectors.
With the successful development of this printer, IIT Jodhpur has opened up new possibilities for the Indian defence and aerospace industries. It has provided them with a cutting-edge technology that can enhance their manufacturing capabilities and enable them to produce high-quality, customized components. This, in turn, will help strengthen the country’s defence and aerospace sectors and contribute to its overall technological advancement.
In conclusion, IIT Jodhpur’s development of an indigenous metal 3D printer for defence and aerospace applications is a significant milestone in India’s journey towards self-reliance in advanced manufacturing technologies. The printer’s capabilities, versatility, and performance make it a valuable asset for the country’s defence and aerospace industries. This achievement not only highlights the technical prowess of IIT Jodhpur but also underscores the potential of Indian institutions to drive innovation and contribute to critical sectors.
Exploring the Potential of Indigenous Metal 3D Printing in Defence and Aerospace Industries
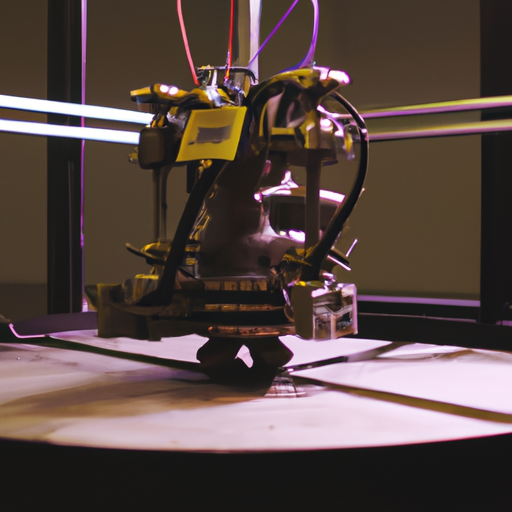
Indigenous Metal 3D Printer for Defence, Aerospace Applications Developed by IIT Jodhpur
In recent years, 3D printing technology has revolutionized various industries, and now it is making its mark in the defence and aerospace sectors. The Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Jodhpur has developed an indigenous metal 3D printer that has the potential to transform the way components are manufactured for these critical industries.
The development of this metal 3D printer is a significant achievement for IIT Jodhpur and the country as a whole. It showcases India’s growing capabilities in advanced manufacturing technologies and highlights the potential for indigenous innovation in the defence and aerospace sectors.
One of the key advantages of metal 3D printing is its ability to produce complex geometries that are difficult or impossible to manufacture using traditional methods. This opens up new possibilities for designing and manufacturing components that are lighter, stronger, and more efficient. In the defence and aerospace industries, where weight reduction and performance are crucial, this technology can have a significant impact.
The metal 3D printer developed by IIT Jodhpur is capable of printing components using a wide range of metals, including titanium, aluminum, and stainless steel. This versatility allows for the production of a variety of components, from engine parts to structural elements. The printer’s high precision and accuracy ensure that the printed components meet the stringent quality requirements of the defence and aerospace industries.
Another advantage of metal 3D printing is its ability to reduce material waste. Traditional manufacturing methods often result in significant material wastage, as parts are machined from larger blocks of material. With 3D printing, only the required amount of material is used, minimizing waste and reducing costs. This is particularly important in the defence and aerospace industries, where material costs can be high.
The development of an indigenous metal 3D printer is also a step towards self-reliance in the defence and aerospace sectors. Currently, many critical components are imported, leading to dependence on foreign suppliers. By developing the capability to manufacture these components locally, India can reduce its reliance on imports and strengthen its strategic independence.
Furthermore, the use of metal 3D printing can also lead to shorter lead times for component production. Traditional manufacturing methods often involve long lead times, as parts need to be machined, assembled, and tested. With 3D printing, components can be produced on-demand, reducing the time required for production and assembly. This can be particularly beneficial in emergency situations or when quick turnaround times are required.
The development of an indigenous metal 3D printer by IIT Jodhpur is a significant milestone in the exploration of the potential of this technology in the defence and aerospace industries. It showcases India’s capabilities in advanced manufacturing and highlights the benefits of metal 3D printing, such as the ability to produce complex geometries, reduce material waste, and shorten lead times.
As the technology continues to evolve, it is expected that metal 3D printing will play an increasingly important role in the defence and aerospace sectors. It has the potential to revolutionize component manufacturing, leading to lighter, stronger, and more efficient systems. With the development of indigenous capabilities, India is well-positioned to take advantage of this technology and strengthen its position in these critical industries.
Revolutionary Applications of IIT Jodhpur’s Indigenous Metal 3D Printer in Defence and Aerospace
Indigenous Metal 3D Printer for Defence, Aerospace Applications Developed by IIT Jodhpur
The Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Jodhpur has recently made a groundbreaking development in the field of 3D printing. They have successfully developed an indigenous metal 3D printer that has revolutionary applications in the defence and aerospace industries. This achievement is a testament to the innovative capabilities of the researchers at IIT Jodhpur and their commitment to pushing the boundaries of technology.
One of the key advantages of this indigenous metal 3D printer is its ability to print complex and intricate designs with high precision. This is particularly important in the defence and aerospace sectors, where components need to be lightweight yet strong enough to withstand extreme conditions. With this new technology, engineers can now design and manufacture parts that were previously impossible to create using traditional manufacturing methods.
The metal 3D printer developed by IIT Jodhpur utilizes a process called selective laser melting (SLM). This involves melting metal powder layer by layer using a high-powered laser, resulting in a solid and fully functional component. The printer is capable of working with a wide range of metals, including titanium, aluminum, and stainless steel, making it versatile for various applications.
In the defence industry, this indigenous metal 3D printer has the potential to revolutionize the production of military equipment. From small components like brackets and hinges to larger parts such as engine components and structural elements, the printer can create them all. This not only reduces the time and cost of manufacturing but also allows for customization and rapid prototyping, enabling faster innovation and development of new technologies.
Similarly, in the aerospace industry, the applications of this metal 3D printer are immense. Aircraft components, such as turbine blades and fuel nozzles, can now be produced with greater efficiency and accuracy. The lightweight nature of 3D printed parts also contributes to fuel efficiency, reducing the overall weight of the aircraft. This technology has the potential to transform the way aircraft are designed and manufactured, leading to more advanced and efficient flying machines.
Furthermore, the indigenous metal 3D printer developed by IIT Jodhpur has the potential to boost the country’s economy. With the ability to manufacture high-quality components locally, India can reduce its dependence on imports and strengthen its domestic manufacturing capabilities. This not only creates job opportunities but also contributes to the growth of the overall manufacturing sector.
In conclusion, the development of an indigenous metal 3D printer by IIT Jodhpur is a significant achievement with revolutionary applications in the defence and aerospace industries. The printer’s ability to create complex and lightweight components with high precision opens up new possibilities for innovation and customization. With this technology, India can strengthen its manufacturing capabilities and reduce its dependence on imports. The future looks promising for the defence and aerospace sectors, thanks to the groundbreaking work of the researchers at IIT Jodhpur.
The Future of Defence and Aerospace Manufacturing: Indigenous Metal 3D Printing by IIT Jodhpur
Indigenous Metal 3D Printer for Defence, Aerospace Applications Developed by IIT Jodhpur
In recent years, 3D printing has revolutionized the manufacturing industry. From creating prototypes to producing end-use parts, this technology has proven to be a game-changer. And now, the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Jodhpur has taken it a step further by developing an indigenous metal 3D printer specifically for defence and aerospace applications.
This groundbreaking development is set to transform the future of defence and aerospace manufacturing in India. With the ability to print complex metal parts with high precision, this technology opens up a world of possibilities for the country’s defence and aerospace sectors.
One of the key advantages of this indigenous metal 3D printer is its ability to produce parts with intricate geometries that are otherwise difficult or impossible to manufacture using traditional methods. This means that designers and engineers can now create components that are lighter, stronger, and more efficient, leading to improved performance and reduced costs.
Moreover, this technology allows for rapid prototyping, enabling faster design iterations and reducing time to market. This is particularly crucial in the defence and aerospace industries, where innovation and agility are paramount. With this metal 3D printer, researchers and manufacturers can quickly test and refine their designs, leading to faster development cycles and ultimately, better products.
Another significant advantage of this indigenous metal 3D printer is its potential to enhance supply chain resilience. Traditionally, defence and aerospace industries heavily rely on imported components, which can be costly and subject to geopolitical risks. By developing this technology domestically, IIT Jodhpur is helping to reduce dependence on foreign suppliers and strengthen India’s self-reliance in critical sectors.
Furthermore, this metal 3D printer has the potential to revolutionize maintenance, repair, and overhaul (MRO) operations in the defence and aerospace sectors. With the ability to produce spare parts on-demand, this technology can significantly reduce downtime and costs associated with sourcing and stocking spare parts. This means that military and aerospace equipment can be repaired and maintained more efficiently, ensuring operational readiness and cost-effectiveness.
The development of this indigenous metal 3D printer by IIT Jodhpur is a testament to India’s growing capabilities in advanced manufacturing. It showcases the country’s commitment to innovation and self-reliance in critical sectors such as defence and aerospace.
Moving forward, it is essential to continue investing in research and development to further enhance the capabilities of this technology. By collaborating with industry partners and leveraging the expertise of academia, India can continue to push the boundaries of metal 3D printing and unlock its full potential for defence and aerospace applications.
In conclusion, the development of an indigenous metal 3D printer by IIT Jodhpur marks a significant milestone in the future of defence and aerospace manufacturing in India. With its ability to produce complex metal parts with high precision, this technology offers numerous advantages, including improved performance, reduced costs, faster design iterations, enhanced supply chain resilience, and more efficient MRO operations. By harnessing the power of 3D printing, India is poised to strengthen its self-reliance and competitiveness in these critical sectors.
